Strategies for Handling Padding in C Programming
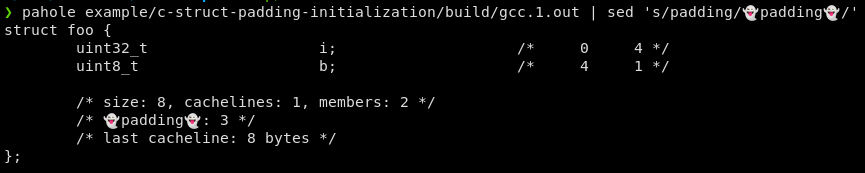
In C programming, padding refers to extra memory added between structure members to align data for efficient CPU access. The compiler adds padding to align members to their natural boundaries. For example, in a 32-bit system:
Here, the compiler adds 3 bytes of padding after "b" to make the structure 8 bytes in total. The article discusses strategies to optimize memory layout and access, focusing on packed structures.
 More information:
More information:
https://interrupt.memfault.com/blog/c-struct-padding-initialization
Here, the compiler adds 3 bytes of padding after "b" to make the structure 8 bytes in total. The article discusses strategies to optimize memory layout and access, focusing on packed structures.
 More information:
More information:https://interrupt.memfault.com/blog/c-struct-padding-initialization