19 Replies
@Dexter
Note for OP
+solved @user1 @user2... to close the thread when your doubt is solved. Mention the users who helped you solve the doubt. This will be added to their stats.thanks for sharing them separately, appreciate it :)
Please share an attempt as well?
Im sorry i did them last night and now im omw to coaching. As soon as i get home i will send
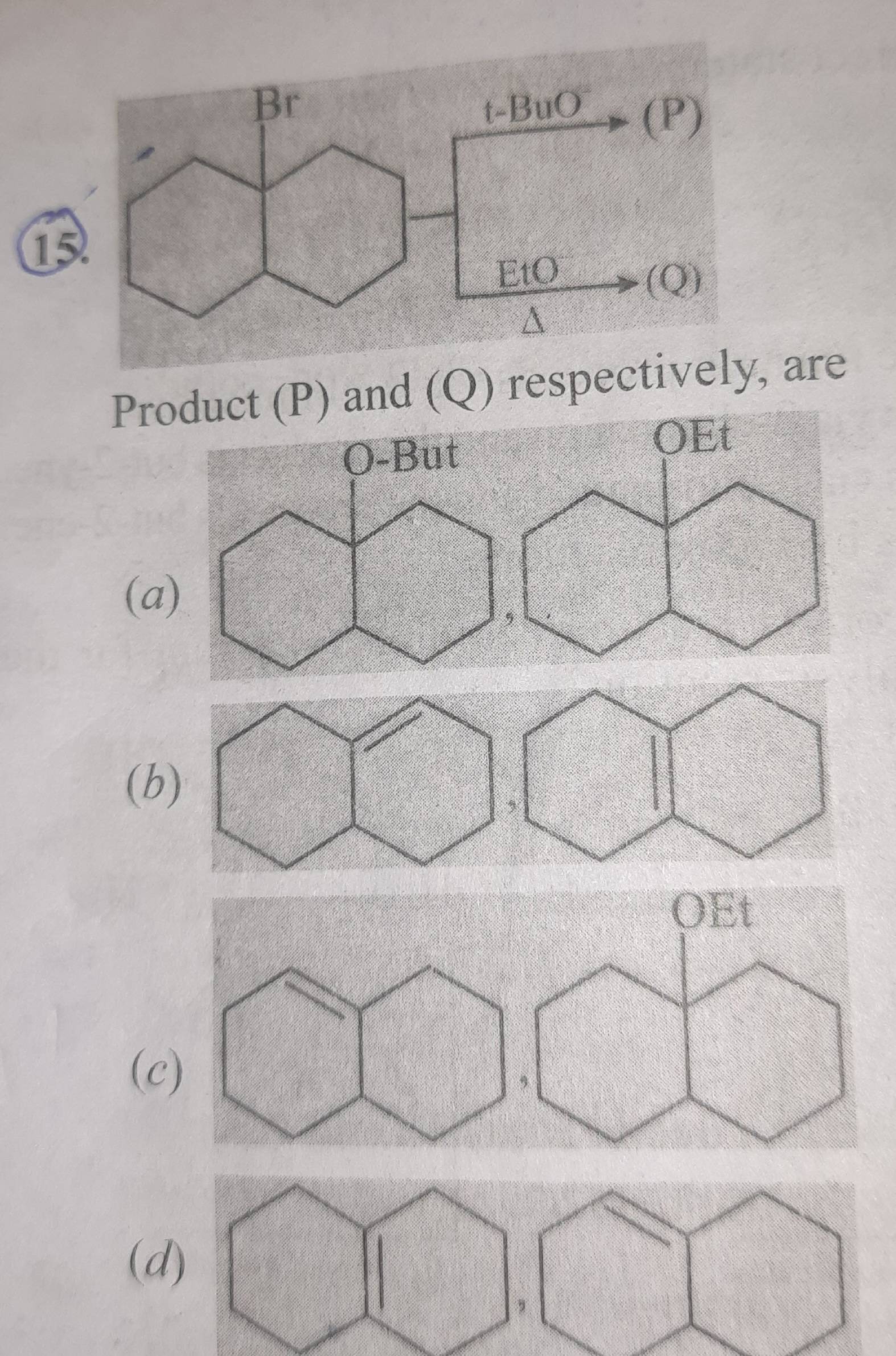
In this one i thought carbocation is at the most stable position so the nucelophile would just get attached
A option according to me but the answer is B
all g buddy
sterically hindered substrate, so elimination is the only option.
gotta choose bw b and c, a gets eliminated
since q is formed on heating, elim again.
and bulky nu:
very bulky
Option B?
Elimination requires heat?
Heat always favours elimination with base
Broooo
.chem
aight imma see that
oh so thats why double bond forms
but how do we confirm if P also goes through elimination.
is it bcz t-but is a strong base?
can someone send the mechanism for this?
Dehydrohalogenation occurs in the presence of strong bases like alcoholic KOH, NaNH2, MeO-, EtO-
Here, we remove anti beta-H
Tertiary butoxide is also a base but it is bulky so it removes the beta-H which is less stearically hindered


+solved @Prachi
Post locked and archived successfully!
Archived by
<@1382187168230936577> (1382187168230936577)
Time
<t:1752715310:R>
Solved by
<@926887811674673172> (926887811674673172)