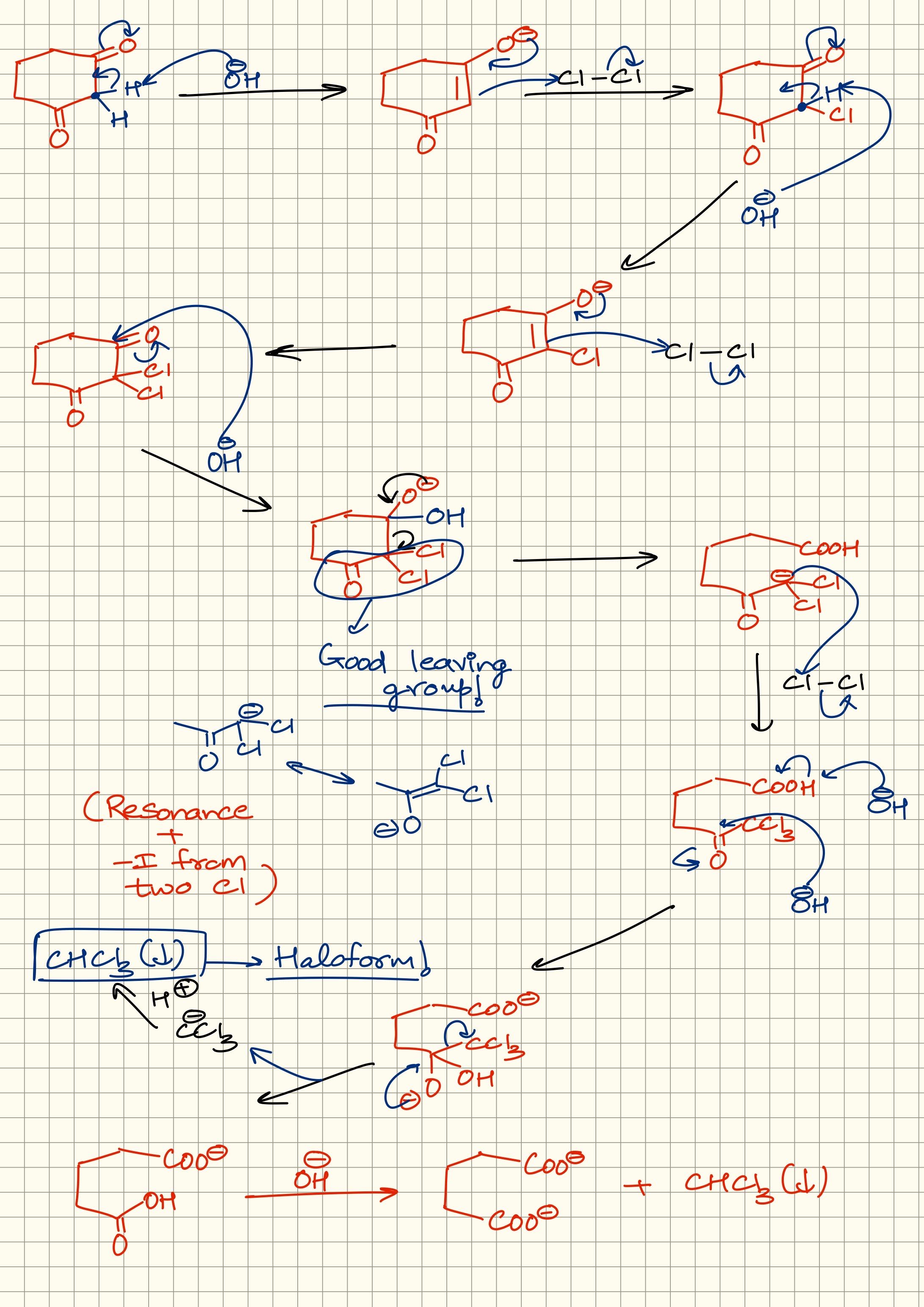
Rest of the mechanism ?
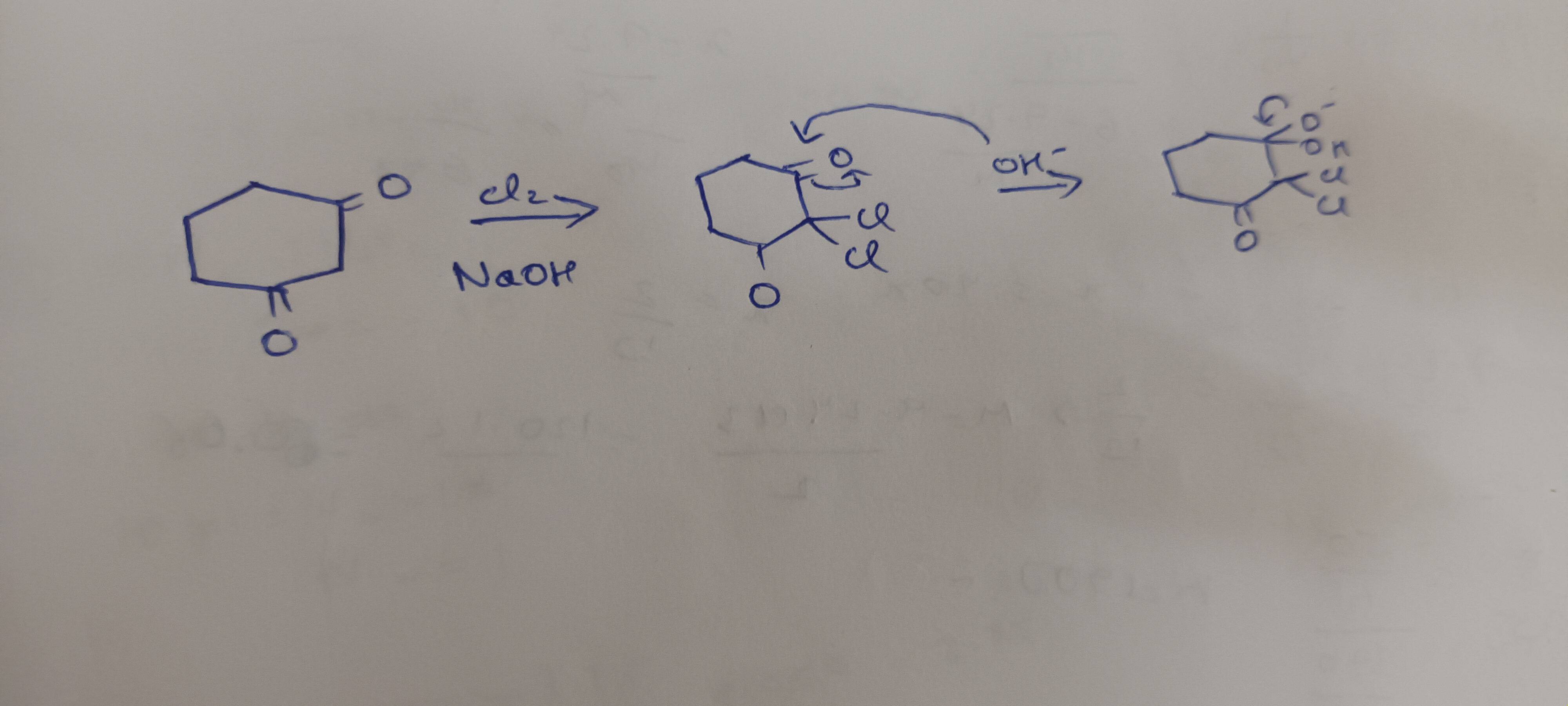
It comes under 1,3 dicarbonyl compounds participating in haloform reactions. (Adv topic form what My sir said.) Give Me an idea or a solution how to solve further ( alcohols phenols and ethers)
19 Replies
@Dexter
Note for OP
+solved @user1 @user2... to close the thread when your doubt is solved. Mention the users who helped you solve the doubt. This will be added to their stats.Kick that C-C bond
Towards the carbon with 2Cl atoms
Negative charge gets stabilised as there are 2 electronegative groups pull electron density
Making it a good leaving group
On top of that
That negative charge is in resonance with the other C=O
Which also further stabilises it
Now
That negative charge
Can further attack on another Cl2 molecule
Doing haloform like it usually does
I can draw it out or elaborate if you want
Konsa
Jo side vaale C=O ka alpha carbon hai
Bich me hai na jo
Acha vo
Jispe 2 Cl lage hain
Fir uspe negative aayega
More stable
Yea haloform
Hojegi
Acha
Plss I need it
@A
Thanks soo much sirr
It's alright buddy
No need to call me sir though
Not as senior as you might I am
🤍 🤍 thnxx
How to close ts thread ?
Write +solved
+solved
Followed by my @
+solved @Enamine
Post locked and archived successfully!
Archived by
<@807942979922559016> (807942979922559016)
Time
<t:1752112767:R>
Solved by
<@984016629119713290> (984016629119713290)