41 Replies
@Gyro Gearloose
Note for OP
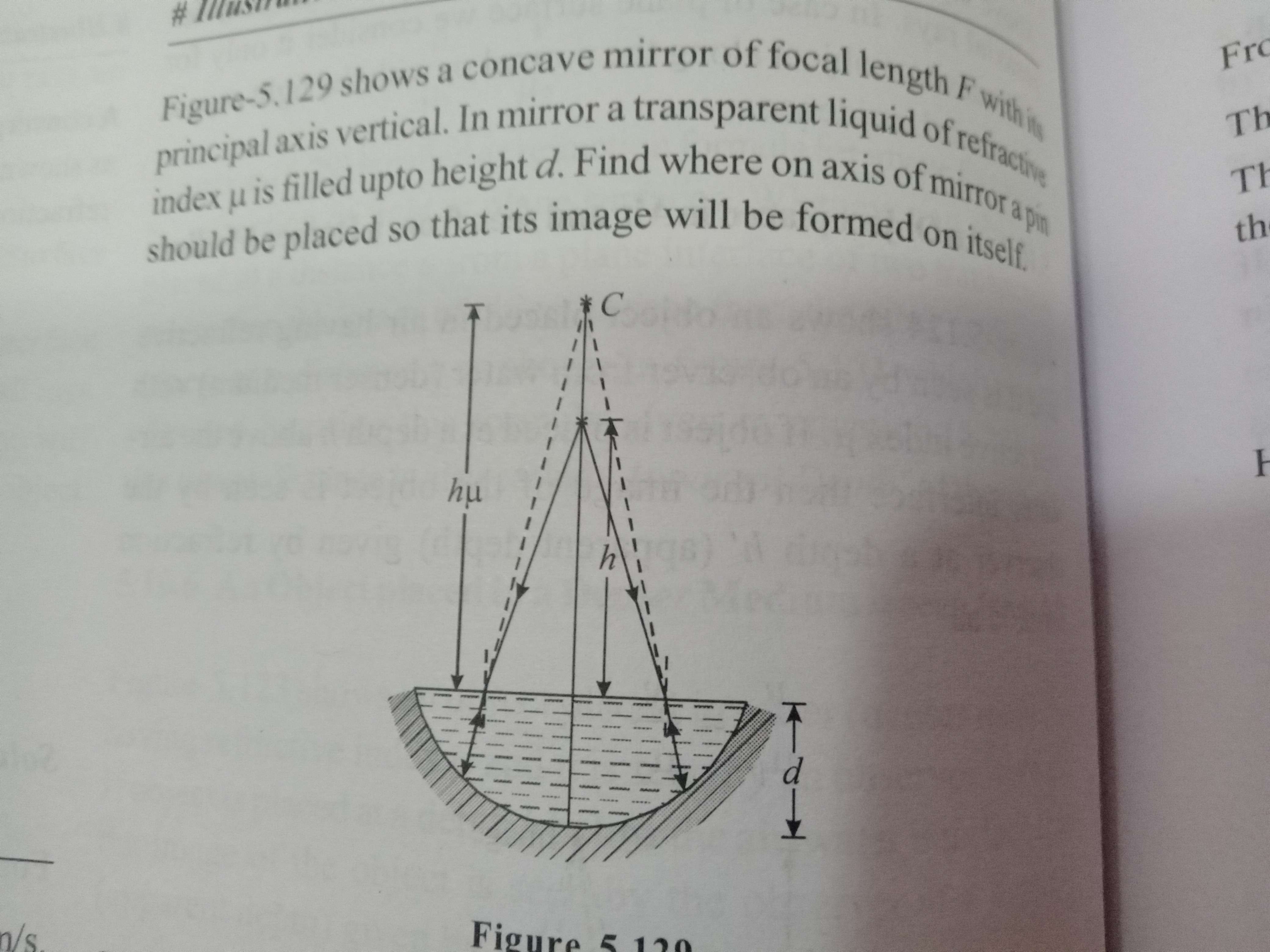
+solved @user1 @user2... to close the thread when your doubt is solved. Mention the users who helped you solve the doubt. This will be added to their stats.let the object be at a height h as shown .
first refraction takes place and an image is formed at a height hu
now reflection takes place with that image as a virtual object
object distance = hu +d
image distance should be h
f given
This must satisfy the mirror formula . solving for h gives a big weird expression
basically for image to be formed on object itself the distance of object from pole should be equal to ROC which is 2f
so here virtual object is at dist u(h)+d from pole
so uh+d=2f
h=2f-d/u
technically my calc should work too right
how can object distance and image distance be different if we want the image to be formed on object itself? here dist of virtual object should be uh+d and dist of image should be same asw, when the light exits the water it bends agaain thus forming the actual image at h
the image formed after refraction is working as virtual object right ?
this object forms the image on the original object
yea after the first refraction there is an image formed at uh+d which acts as our virtual object, but ur forgetting that light will bend again as it leaves the water which means the image should form on the virtual object itself, and onc the light leaves the water and bends again, it will automatically adjust thus forming the actual image at h
ohh
so after first refraction image is formed at uh
now reflection takes place
object dist = uh+d , focal length f we find v using mirror formula
now again refraction takes place and now the image must form at the point original object was placed
h = (d-v)/u
it should be v-d/u since thats the height above surface of liq
v is measured from pole
fir bhi nahi a rha
v ko put kro 2f cuz radius of curvature
whats the ans

😭
put v as 2f cuz que says image object pe hi banna chaihe which only happens when object/image is both at 2f😭

i am trying to not utilise this fact
this would imply that final image is directly obtained after reflection
but it goes refraction -> reflection -> refraction
look hame final image h pe banani he right?
after the 2nd refraction yes
by what i did image is formed at uh+d after reflection
then it will refract again
and it will finally form at h
didnt u just make img at 2f with object at uh+d
its the same here 😭 cuz object 2f pe rakha hona chaihe for image to be formed on itself so 2f=uh+d
this is the short method
look wait ive got a easier method
as i said i dont wanna utilise this (yet)
i wanna do it by the long approach first
and then get to shorter methods
oh what is ur plan for the long apraoch?
like actually ho kaise + kyu rha hai
what ive done here
the entire procedure goes like refraction -> reflection -> refraction
original object is at h from water surface after first refraction image at uh from water surface this serves as virtual object for mirror object distance = -(uh +d) , focal length = -f we get some v using mirror formula now finally refraction takes place again with the image formed in previous step as object. here image should be obtained at h from surface h = (v-d)/u this is the long approach
original object is at h from water surface after first refraction image at uh from water surface this serves as virtual object for mirror object distance = -(uh +d) , focal length = -f we get some v using mirror formula now finally refraction takes place again with the image formed in previous step as object. here image should be obtained at h from surface h = (v-d)/u this is the long approach
okay then what u wrote is correct js put a negative sign in frotn of v as we know its neg and we want its positive value

and then solve for h in this huge expression
u should arrive at this quadratic and solving it for positive root will give the answer
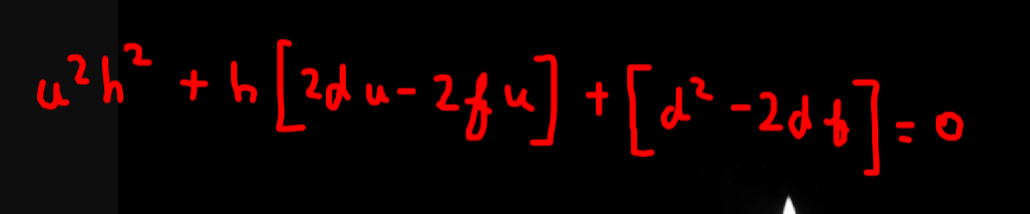
how can we just put a -ve sign acc to our convenience
sign convention matters
since v is on same side of u it will have same sign of u asw which is negative so what we got v is of neg value for example -20cm but in apparant depth formula we always put positive values so we take mod of that which is 20, or we can just put a neg in frotn of v which is -(-20) = 20
putting a - sign shouldnt be necessary for that since we dont know if is greater than uh+d or not
h = (-v-d)/u also seems messed up since we are supposed to take dist from water surface
wait were we supposed to take object distance as +ve if it was virtual
or smthing like that
the distance when u use mirorr formula is always measured from pole, and we take direction of incident light frm object as our positive direction always and here clearly incident light is traveling downard so thats our pos direction, meanwhile object dist and image dist BOTH are upwards from pole hence both are negative
it dosent depend if its greater than uh+d or not
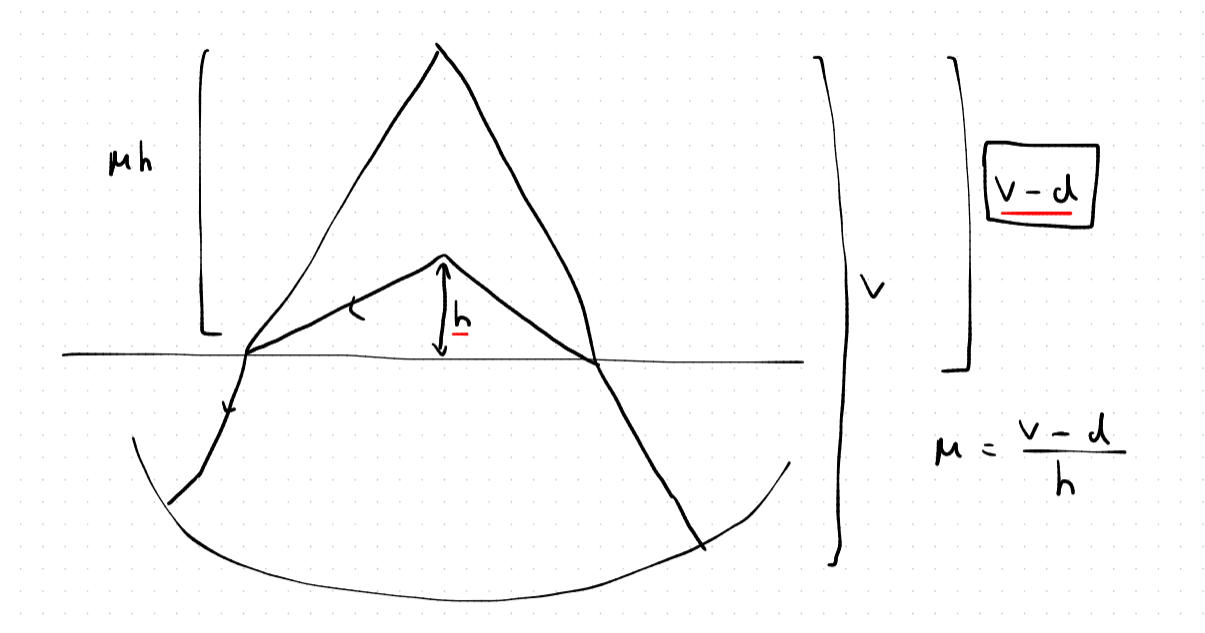
there are no * sign conventions * when using apparant depth formula , we put everything as potivie if thats wha u mean
hmm i get your point now
yea from the formula u get smth like -20cm th eminus js tells u that its upward from pole ant nth else, for apprant depth u have tot ake the actual mag
is this because of the symmetry of the situation .
light rays fall from an object at height h which form an image at hu . now we want hu+d to be 2f cuz then image due to reflection would have formed at hu+d but the light rays refract by the same magnitude as they did in step 1
yea exactly basically for image to be forme don itself type situation, we want incident lays to finally meet at the same point from they originated
here incident rays originated from height h and after refraction as they hit the walls of mirror we want them to retrace their path togo back after another refraction to the same spot... and the light only retraces its incoming path when incidnet rays come from ROC aka object is at 2f
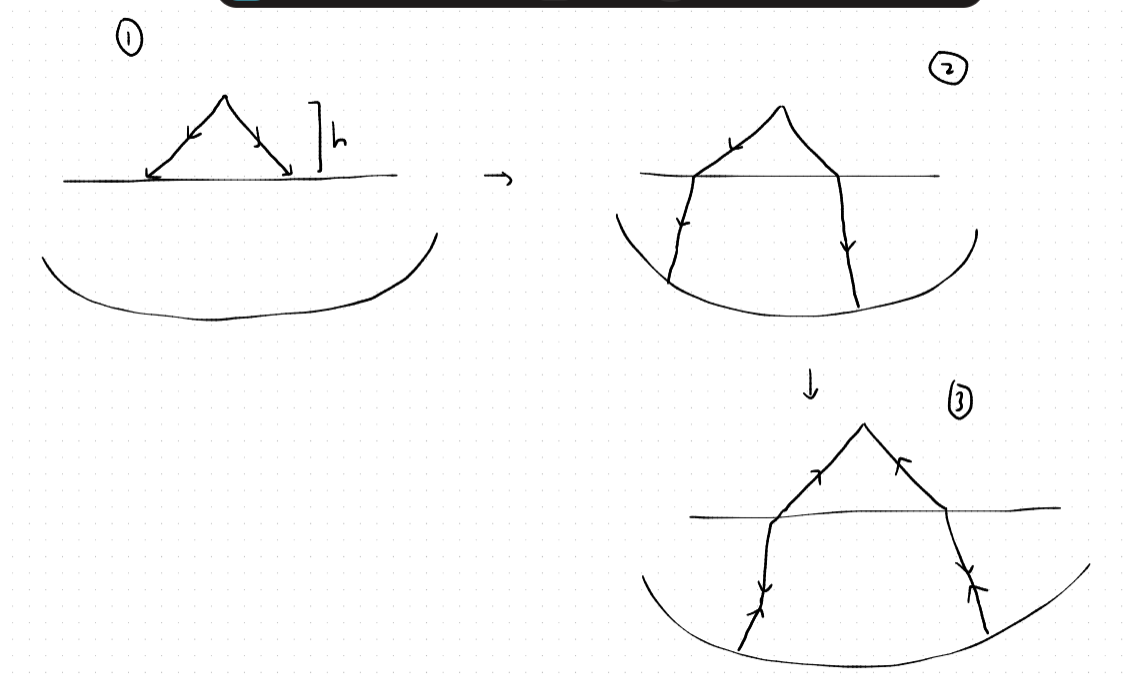
got it
big thanx
+solved @integralofe^2v
Post locked and archived successfully!
Archived by
<@741159941934415883> (741159941934415883)
Time
<t:1758648416:R>
Solved by
<@813025027611688970> (813025027611688970)