an env variable
could it be that in 
process.env
I think what happened is the nextjs dev server loaded
.envprocess.envyeah, it does that 

I had it in
.envok yeah that makes sense then 



@conqr ᯅ I'll improve our error message to remind developers to use the edge runtime  , hopefully this can help avoid developers confusion/frustration: https://github.com/cloudflare/next-on-pages/issues/674
, hopefully this can help avoid developers confusion/frustration: https://github.com/cloudflare/next-on-pages/issues/674
 , hopefully this can help avoid developers confusion/frustration: https://github.com/cloudflare/next-on-pages/issues/674
, hopefully this can help avoid developers confusion/frustration: https://github.com/cloudflare/next-on-pages/issues/674GitHub
We've recently made the getRequestContext local error more helpful, reminding people to set up the dev platform: next-on-pages/packages/next-on-pages/src/api/getRequestContext.ts Lines 52 to 61...
Still learning next, so I forget this quite often 

yeah.... but it's not your fault, it's the problem of Next.js always defaulting to node.js 

some versions back they did allow you to globally specify the edge runtime and have it applied to all your routes!
I so wish they didn't remove that 

You don't cache pages when you do SSR? That doesn't make sense to me.
Take for example a site with 10s of thousands of pages...it wouldn't be efficient to statically generate them all, so they would be generated server side and the response would be cached at the edge. This way the next request comes from cache vs generating it again
Take for example a site with 10s of thousands of pages...it wouldn't be efficient to statically generate them all, so they would be generated server side and the response would be cached at the edge. This way the next request comes from cache vs generating it again
What would this be caused by?
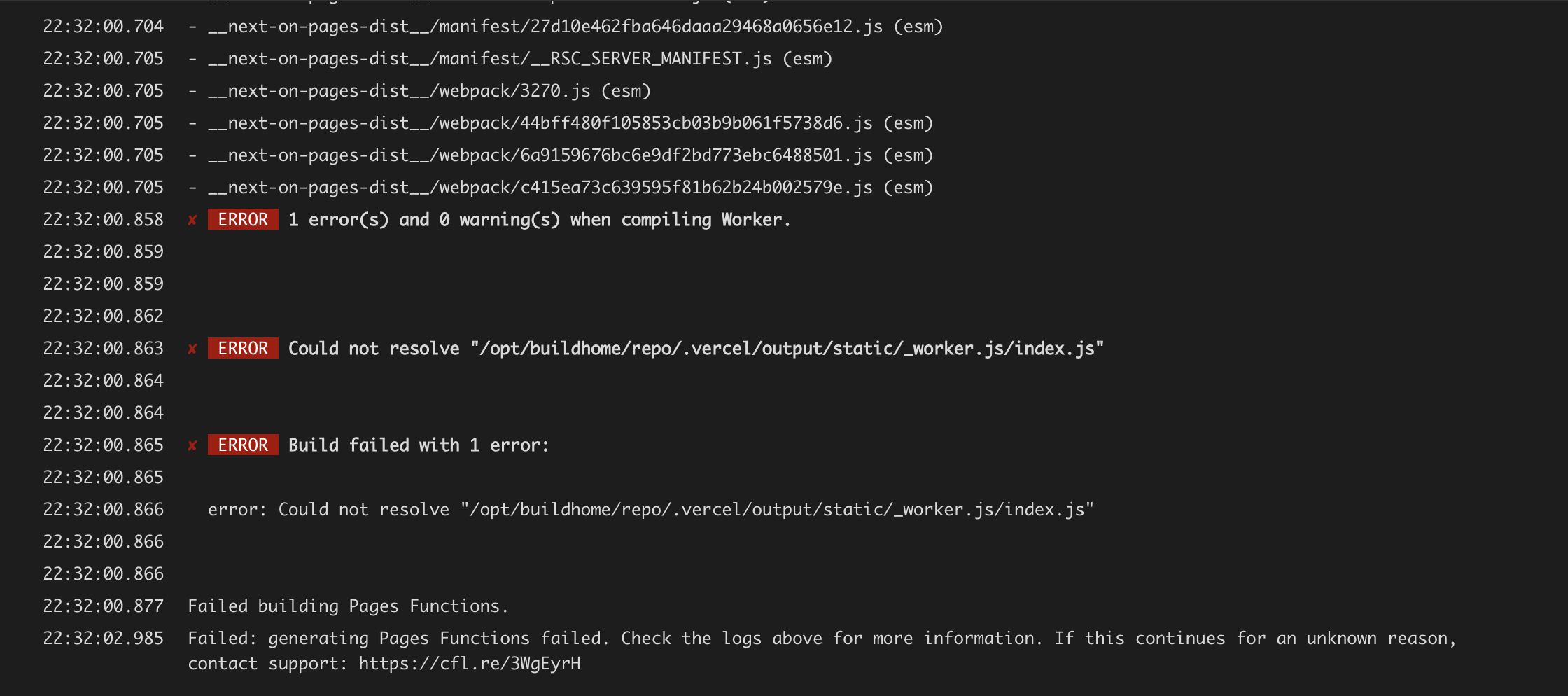
Seems like NPM package htmlrewriter caused the issue :(
the site is deployed, but i am getting 404 error. this is the url: https://testing.client-6ek.pages.dev/
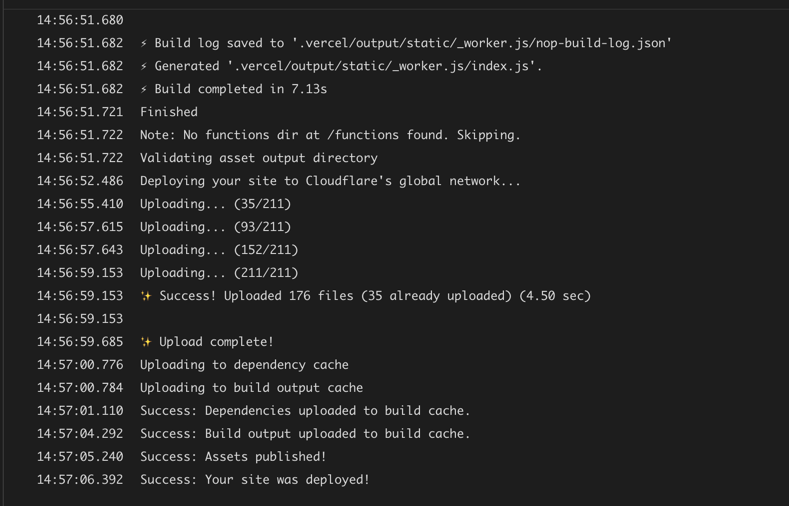
ok, so i deleted the project and did it again, i got the worker limit error
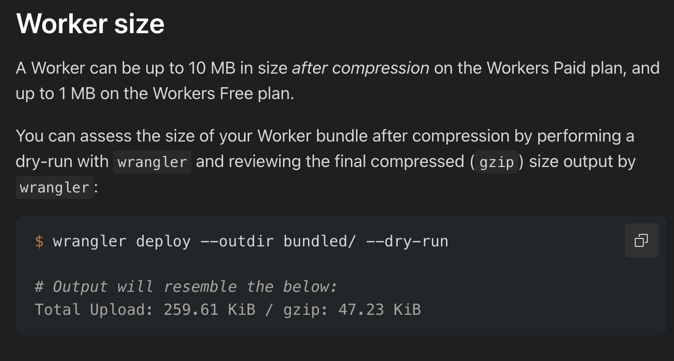
but when i ran this command
it showed me this size. not sure what the issue here is
❯ yarn wrangler deploy .vercel/output/static/_worker.js/index.js --dry-run --compatibility-date 2024-02-22 --name testit showed me this size. not sure what the issue here is
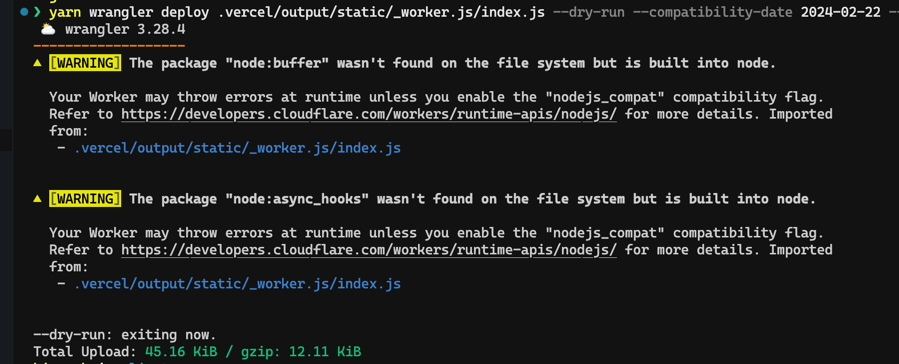
Did you set the nodjs_compat flag?
yes
you should use 
wrangler pages deploywrangler deploy
actually i was following your guide. but ok
https://github.com/cloudflare/next-on-pages/issues/523 this link took me to this page. https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/platform/limits/#worker-size hence the confusion
got this error.
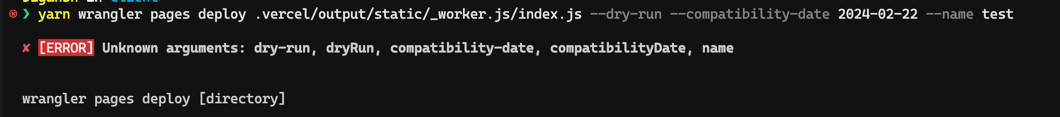
no sorry.... you are going to face the worker-size limit no matter what you use
I was just saying that regarding the last error (the
I was just saying that regarding the last error (the
node:async_hooks one), it's likely due to using the wrong commanddo we tell users to run  if so please let me know as that needs amending!
if so please let me know as that needs amending! 
wrangler deploy if so please let me know as that needs amending!
if so please let me know as that needs amending! 
check the second link. it tells user to run wrangler deploy with dryrun to check the size
yes... but that's
but yeah I guess we should have the same information in the
WorkersPagesbut yeah I guess we should have the same information in the
Pages
yes. worker limit for pages is an extremely common issue. i have pinged this chat 100s of times with same request coz it is very arbritary.
but the issue at hand right now, how do i check my worker size for the nextjs site?
can you remove the cli arguments? (since they are not supported in
wrangler pages deploythat will deploy the website. i dont want to do that. just want to check the size
basically the only thing (as far as I remember) is to build the worker 
@cloudflare/next-on-pages.vercel/output/static/_worker.js
ok, so its 1.5 mb
oof
with the paid tier the limit goes up to 10 MB by the way 

How do you get the env in a non request?
Example in my case:
Example in my case:
How do you get the env in a non request?all your source code is run inside a Cloudflare worker request handler, so you're basically always handling a request (i.e. you should always be able to run
getRequestContextYea thats what I thought aswell just getting this error when building:
Error: Error: failed to retrieve the Cloudflare request context
12:31:26.281 ▲ at u (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:352:2658)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at 73355 (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:347:27369)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at webpack_require (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/edge-runtime-webpack.js:25:42)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at /opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:381:4970
12:31:26.281 ▲ at webpackJsonpCallback (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/edge-runtime-webpack.js:208:39)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at /opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:1:51
12:31:26.281 ▲ at Script.runInContext (node:vm:135:12)
12:31:26.282 ▲ at runInContext (node:vm:283:6)
12:31:26.282 ▲ at evaluateInContext (/opt/buildhome/repo/node_modules/next/dist/server/web/sandbox/context.js:377:38)
12:31:26.282 ▲ at getRuntimeContext (/opt/buildhome/repo/node_modules/next/dist/server/web/sandbox/sandbox.js:70:9)
12:31:26.282 ▲ > Build error occurred
12:31:26.284 ▲ Error: Failed to collect page data for /api/auth/[...nextauth]
12:31:26.284 ▲ at /opt/buildhome/repo/node_modules/next/dist/build/utils.js:1258:15
12:31:26.284 ▲ at process.processTicksAndRejections (node:internal/process/task_queues:95:5) {
12:31:26.284 ▲ type: 'Error'
Error: Error: failed to retrieve the Cloudflare request context
12:31:26.281 ▲ at u (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:352:2658)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at 73355 (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:347:27369)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at webpack_require (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/edge-runtime-webpack.js:25:42)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at /opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:381:4970
12:31:26.281 ▲ at webpackJsonpCallback (/opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/edge-runtime-webpack.js:208:39)
12:31:26.281 ▲ at /opt/buildhome/repo/.next/server/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route.js:1:51
12:31:26.281 ▲ at Script.runInContext (node:vm:135:12)
12:31:26.282 ▲ at runInContext (node:vm:283:6)
12:31:26.282 ▲ at evaluateInContext (/opt/buildhome/repo/node_modules/next/dist/server/web/sandbox/context.js:377:38)
12:31:26.282 ▲ at getRuntimeContext (/opt/buildhome/repo/node_modules/next/dist/server/web/sandbox/sandbox.js:70:9)
12:31:26.282 ▲ > Build error occurred
12:31:26.284 ▲ Error: Failed to collect page data for /api/auth/[...nextauth]
12:31:26.284 ▲ at /opt/buildhome/repo/node_modules/next/dist/build/utils.js:1258:15
12:31:26.284 ▲ at process.processTicksAndRejections (node:internal/process/task_queues:95:5) {
12:31:26.284 ▲ type: 'Error'
The code you're sharing seems fine to me... I'd need to see how you're using it to see what might be going wrong 
PS: also we do have a current bug that prevents

PS: also we do have a current bug that prevents
drizzle
Fully prevents drizzle from working? Or certain functions?
ah yeah I see... that means that that code is getting run by Next.js during the build process to pre-render something....
is that file always only imported in routes using the edge runtime? (because if it is I would assume that Next.js should not error here )
)
this might be an actual Next.js + next-on-pages bug/limitation... (I'd have to look into it further...) one thing you could do as a workaround would be to use
(I'd have to look into it further...) one thing you could do as a workaround would be to use
is that file always only imported in routes using the edge runtime? (because if it is I would assume that Next.js should not error here
 )
)this might be an actual Next.js + next-on-pages bug/limitation...
 (I'd have to look into it further...) one thing you could do as a workaround would be to use
(I'd have to look into it further...) one thing you could do as a workaround would be to use getOptionalRequestContextfully... I think.... I am not too sure to be honest 
anyways the bug that most likely causes it not to work has been fixed in our runtime (https://github.com/cloudflare/workerd/pull/1665/) so hopefully it should work fine after the next runtime release (in a week or two)

anyways the bug that most likely causes it not to work has been fixed in our runtime (https://github.com/cloudflare/workerd/pull/1665/) so hopefully it should work fine after the next runtime release (in a week or two)
I managed to get next-on-pages -> drizzle -> d1 working with next auth for creating my users, so it was working fine for me? Weird
But when I was using process.env it worked on production but not locally and now that I am using env and getRequestContext it works locally but not in production lol
But when I was using process.env it worked on production but not locally and now that I am using env and getRequestContext it works locally but not in production lol
I managed to get next-on-pages -> drizzle -> d1 working with next auth for creating my users, so it was working fine for me? Weirdok, maybe sometimes/in some cases it works.... I really don't know to be honest

 (but if it works for you great!
(but if it works for you great!  )
)But when I was using process.env it worked on production but not locally and now that I am using env and getRequestContext it works locally but not in production lol
I had this exact conversation yesterday

is that you're using variables in a
.envnext devwrangler pages devI see that this PR has been merged, maybe it is already fixed or is it not in prod yet?
no, I'm sure it is not in prod as they haven't released it yet (https://github.com/cloudflare/workerd/releases)