What's the highest token count LLM available on workers ai?
What's the highest token count LLM available on workers ai?

Argument of type '"@hf/thebloke/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct-awq"' is not assignable to parameter of type 'BaseAiImageToTextModels'. typescript (2769) [84, 37]// @ts-expect-error@cf/mistral/mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2-lora has a context (and total limit) of ~15k tokens and you don't need a LoRA to run it.@cf/lykon/dreamshaper-8-lcmdoesn't support passing an image. try @cf/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5-img2img if you want to do image-to-image.


json_format response with workers AI? (like what OpenAI supports) { question: "string", answer: "string" }{question: "what is the best dog", answer: "all of them"} (made this up  )
)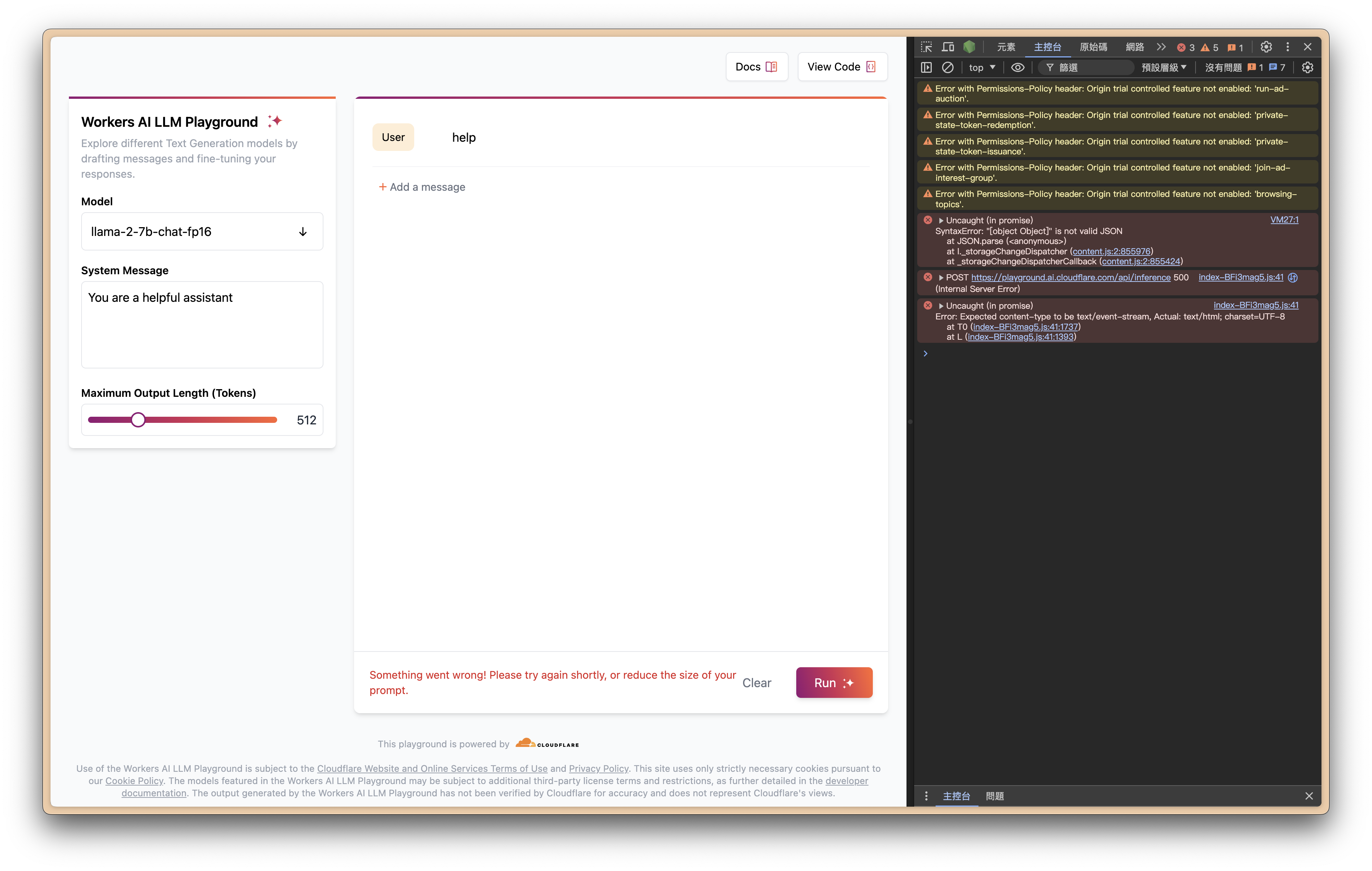
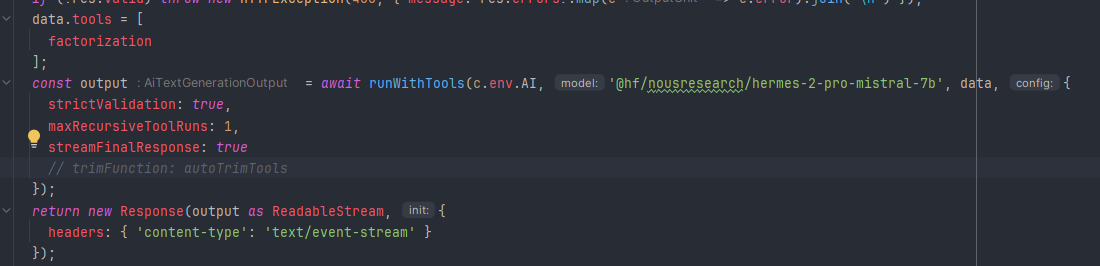
Argument of type '"@hf/thebloke/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct-awq"' is not assignable to parameter of type 'BaseAiImageToTextModels'. typescript (2769) [84, 37]// @ts-expect-error@cf/mistral/mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2-lora3010: Invalid or incomplete input for the model: model returned: [request id: 41fff8e6-617c-439f-a093-f02bfa2d45bb] unexpected shape for input 'image' for model 'dreamshaper-8-lcm'. Expected [1], got [1,1048265]. @cf/lykon/dreamshaper-8-lcm@cf/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5-img2imgjson_format{ question: "string", answer: "string" }{question: "what is the best dog", answer: "all of them"}export const factorization = tool({
description: 'Prime factorize any number even if they are very large',
parameters: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
number: {
type: 'string',
description: 'the number to factorize'
}
},
required: ['number']
},
name: 'factorize-num',
async function({ number }) {
console.log('huh', number);
return await factorize(number);
}
});{
"response": "The number you've provided, 1203210203982198283, is a large number and appears to be an integer. However, finding the prime factorization of such a large number is not practical to do by hand, as it typically involves the use of specialized algorithms and computational resources. \n\nIn general, the factorization of large numbers is often done using numerical methods or mathematical software, such as the quadratic sieve, trial division, or Lenstra elliptic curve factorization, methods typically employed in cryptography or number theory research.\n\nFor all practical purposes, we would use computational tools to find the prime factorization of this number. To get an approximate factorization, you might use an online calculator or a programming language like Python with a library that supports number theory, such as `sympy`:\n\n\`\`\`python\nimport sympy as sp\n\nnumber = 1203210203982198283\n_factors = sp.factorint(number)\n_factors\n\`\`\`\nYou would need to run this code in an environment where you have the `sympy` library installed.\n\nIf you just want to know if it's a prime number, you should also consider that finding the factorization of a very large number to determine primality is computationally expensive, and for such a large number, it's highly unlikely to be a prime.\n\nIf you're seeking a prime factorization for educational purposes or a specific reason, please provide more context, and I can try to help further. Otherwise, it's best to use specialized software or an online tool to get the factorization."
}