I
iTeachChem
A Study Community for Everyone and Everything. We have weekly sessions on Spirituality, Math and Science! JEE, NEET prep? All doubts are crowdsourced. Hare Krishna!
JoinI
iTeachChem
A Study Community for Everyone and Everything. We have weekly sessions on Spirituality, Math and Science! JEE, NEET prep? All doubts are crowdsourced. Hare Krishna!
JoinQUANTUM NUMBER
Why in unielectron species the energy level of subshells in the same shell are same while they vary in multielectron species? Like why doesn't the energy level depend on the angular quantum number
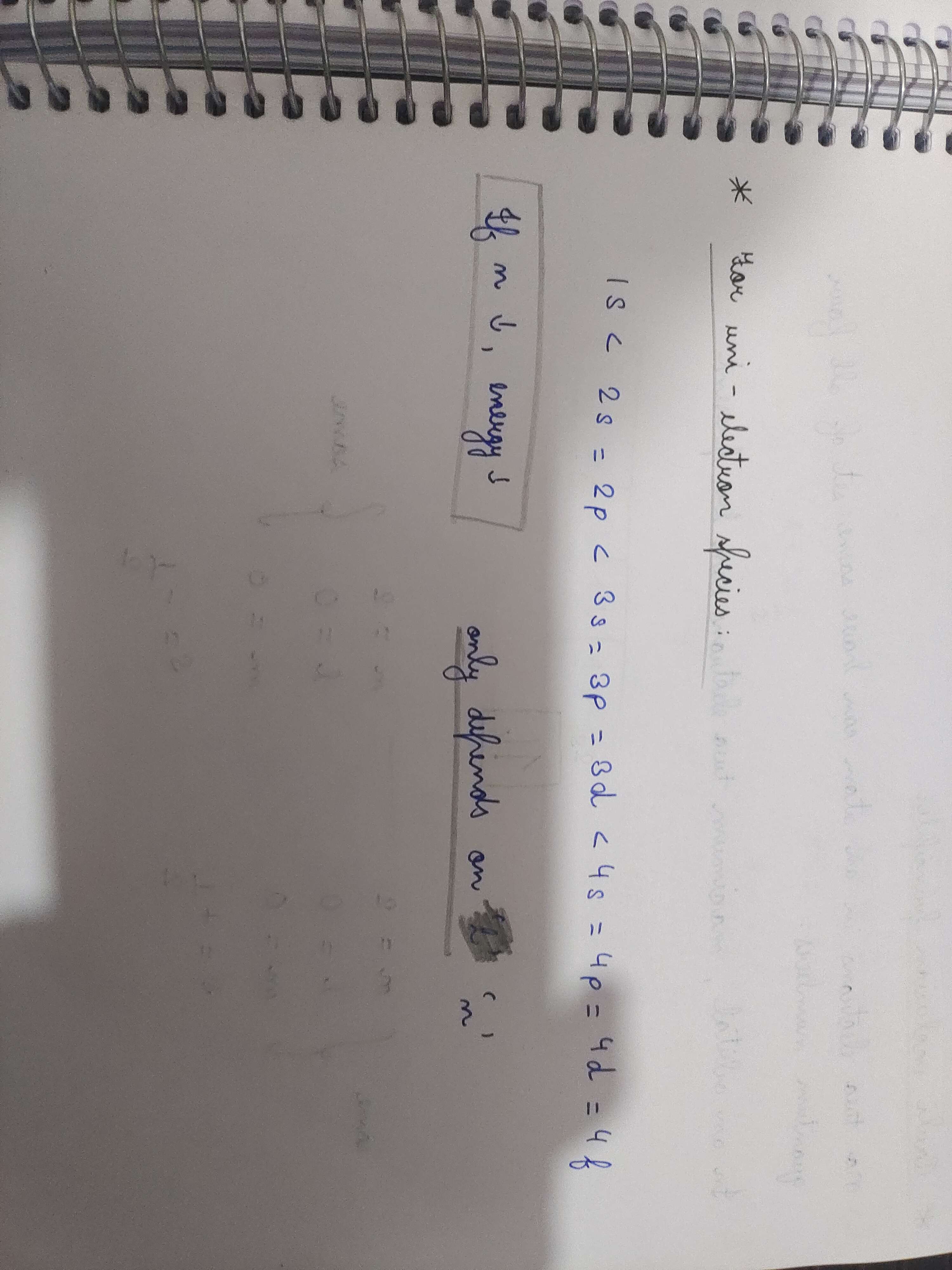
Optical isomerism
uhm so if a compound has a double bond but the rest of the chain is having all sp3 carbons then will it have optical isomerism? and does cyclic comppound have isomerism? if yes how?
aod 2
shouldnt ans of 19th be infinite? (2n pi, (2n+1)pi should be general solution)
what did they do in 20th? shouldnt there be infinite solutions having x1x2 = 1...

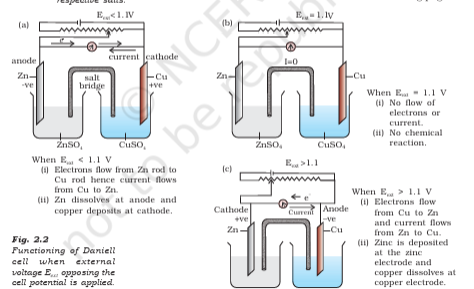
electrochem doubt
I have trouble understanding this portion. Like I understand the changes that occur as we vary the supply potential as illustrated in this diagram from the NCERT. Why does the switching over of cathode and anode take place though? Like Zn, which was initially the anode, after the supply voltage exceeds 1.1V, starts behaving like a cathode. Why so?
I don't understand the chapter well enough, so please explain in detail....